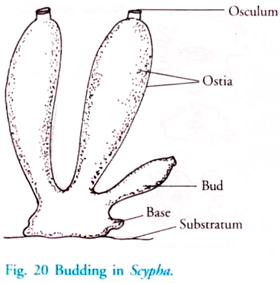
Describe Asexual Reproduction in Sponges by Budding
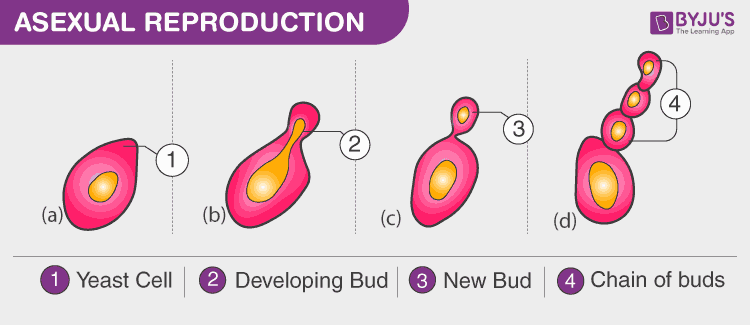
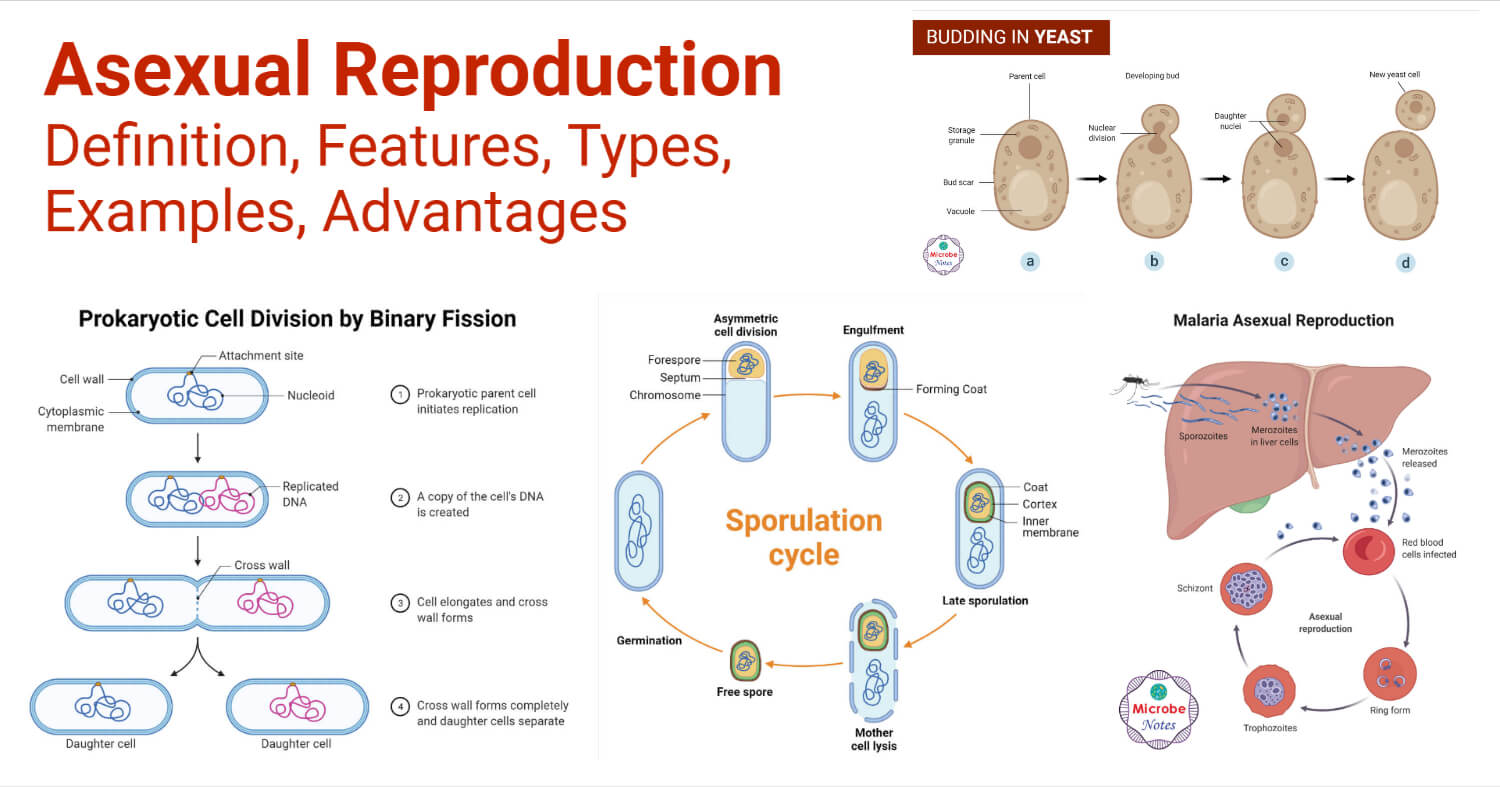
By Formation of Reduction Bodies. Visually describe budding in yeasts.

Ii Phylum Porifera Sponges Sponges Are The Simplest
Sponges reproduce asexually or sexually.
. Describe asexual reproduction in sponges By budding How do sponges avoid self from BSC 2011L at Broward College. This new outgrowth remains attached to the original sponge and separates from the parent organism only when it is mature. Sexual reproduction involves fusion of gametes.
Asexually reproduction is achieved by way of budding which is a process in which new sponges grow out of adult sponges. The asexually reproduction occurs in a process called budding. It floats around for a few days and then sticks to a solid to begin its growth into an adult sponge.
Asexual reproduction is the type of reproduction where offspring are produced without the fusion of male and female gametes. Freshwater sponges as well as several marine species form resistant structures called gemmules that can withstand adverse conditions such as drying or cold and later develop. 1 BY BUDDING 2 BY REGENERATION 1 Budding.
There are 2 types of reproduction in Sponges. It is a type of asexual reproduction where an outgrowth on the surface of the parents body is specialized and separated and developed into a new individual. Asexual reproduction is generally used in less complex species and is quite efficient.
Describe the asexual reproduction of sponges budding and fragmentation budding. Asexual reproduction only requires a single parent that will pass down all of its genes to the offspring. Describe the sexual reproduction of monoecious sponges.
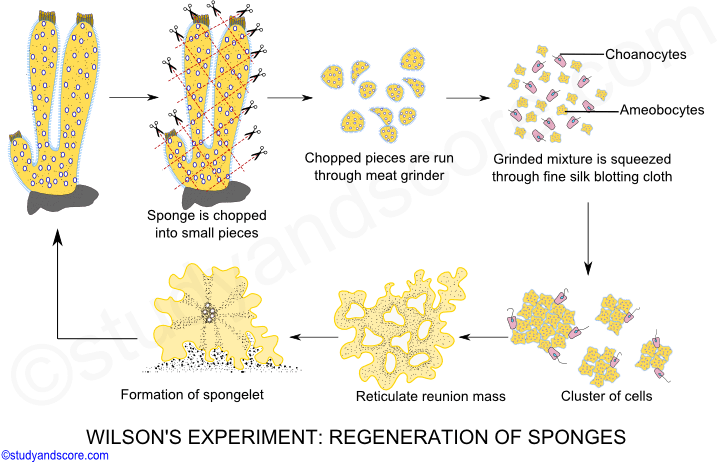
This method is common in many plants Some animals such as sponges and Hydra and sea star starfish Some worms such as Planaria The capacity for regeneration decreases by increasing the animals evolution. All sponges possess a remarkable ability to regenerate lost parts. This means there is no mixing of genes and the offspring is actually a clone of the parent barring any sort of mutations.
Sponges may also reproduce asexually. Sycon shows two types of reproduction namely. Most sponges are hermaphrodites possessing both eggs and sperm.
Sexual reproduction involves fusion of gametes. Asexual reproduction includes budding reduction bodies and gammae in sponges. Sponges reproduce asexually or sexually.
Insects sponges jellyfish worms. By Formation of Gemmules. Asexual reproduction in sponges is by.
Up to 24 cash back The Stove Pipe Sponge reproduces both sexually and asexually. Regeneration - Replacement of lost body parts - The Planaria can regrow part of its body. Sponges show asexual reproduction by the following methods.
A piece cut from the body of a sponge is capable of growing into a complete sponge. In asexual reproduction a small sponge will grow off the side of the parent sponge in a process called budding. Gametes develop from the differentiation of either choanocytes or amoebocytes depending on the species.
It may also be achieved asexually by fragmentation in which a detached piece of an adult sponge develops into a new organism. Asexual reproduction occurs by budding or by fragmentation. Habitat fragmentation means that many species occur in discrete populations1 so it is important for sessile species to colonize new areas.
Budding occurs when a new organism develops from an outgrowth of an existing one. Internal sponge cells become covered in a tough coating. When the conditions are favorable small projections arise.
An outgrowth from the sponge body wall may arise either at the base or near the attached end. Some species will bud internally by packing the new sponge cells into vesicles called gemmules which are released into the water when the parent sponge dies. This kind of asexual reproduction is found in some protozoans.
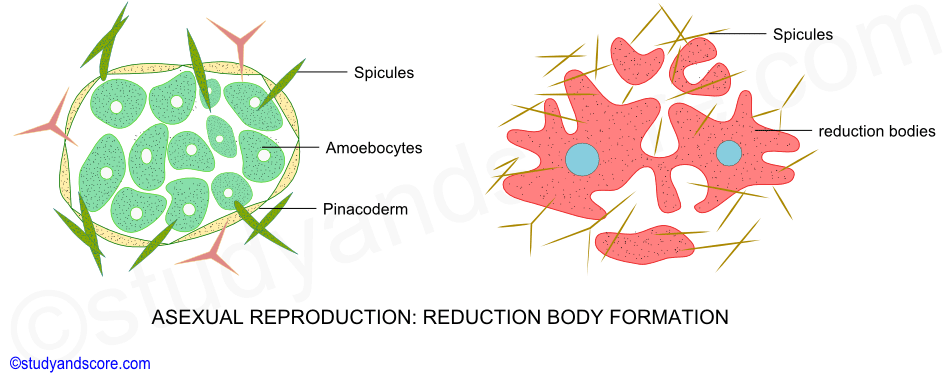
Gemmules survive adverse conditions. Budding is a second method of asexual reproduction in sponges. Asexual reproduction includes budding reduction bodies and gammae in sponges.
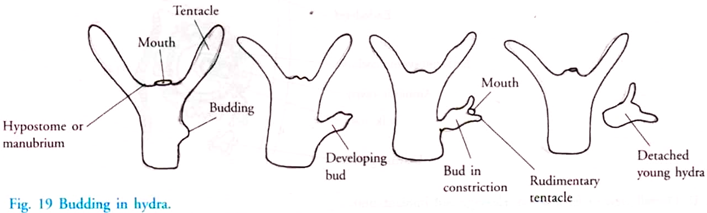
Budding in biology a form of asexual reproduction in which a new individual develops from some generative anatomical point of the parent organism. Freshwater sponges like Spongilla and. They produce clones through mitosis.
Describe bees in asexual reproduction. Formation of gemmules Budding. Sperm produced by the male sponge one that is producing sperm at the time of reproduction is concentrated and released into the aquatic environment through the oscula.
Describe the asexual reproduction of sponges during gemmulation in freshwater. The body of sycon is highly branched. In some species buds may be produced from almost any point of the body but in many cases budding is restricted to specialized areas.
All sponges that are produced asexually are exact clones of the parent sponge. The buds may remain attached to the parent or separate from it and each bud develops into a new individual. Sponges are also able to reproduce asexually through budding.
In multiple fission the nucleus first divides by mitosis to form many nuclei and then the cytoplasm divides according to the number of nuclei. By this method the number of individuals in the colony may increase or new colonies may be formed. Budding another form of asexual reproduction is when sponges grow an external copy of themselves or a bud that is either released or broken off by the current and grows into a.
Gemmules are the asexual. They can grow new individuals from one cell. Regeneration is not considered as a reproduction in some organisms where it.
Higher animals regeneration for compensation. In binary fission parent cells divides into two identical daughter cells by mitosis. REPRODUCTION TYPES IN SYCON SPONGE.
Fragmentation- regenerate when broken. It consists of 3 stages. It has not been clear how sponges whose larvae disperse.
It is of 5 types. Larvae After fertilization in the sponge a larva is released into the water. ASEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN SPONGES.
Porifera members can grow an external bud which eventually breaks off. Formation of reduction bodies. This kind of asexual reproduction is found in Amoeba.
Reproduction In Animals Asexual And Sexual With Diagram Zoology

Chapter 26 Sponges And Cnidarians Ppt Video Online Download
Modes Of Reproduction Asexual And Sexual Reproduction Byju S

Sponge Reproduction Advanced Ck 12 Foundation

Phylum Porifera Reproduction Classification How Do Sponges Reproduce Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Phylum Porifera Sexual And Asexual Reproduction In Sponges And Regeneration In Sponges Study Score
Unit 5 1 Phylum Porifera The Biology Classroom

Sponge Reproduction Advanced Ck 12 Foundation
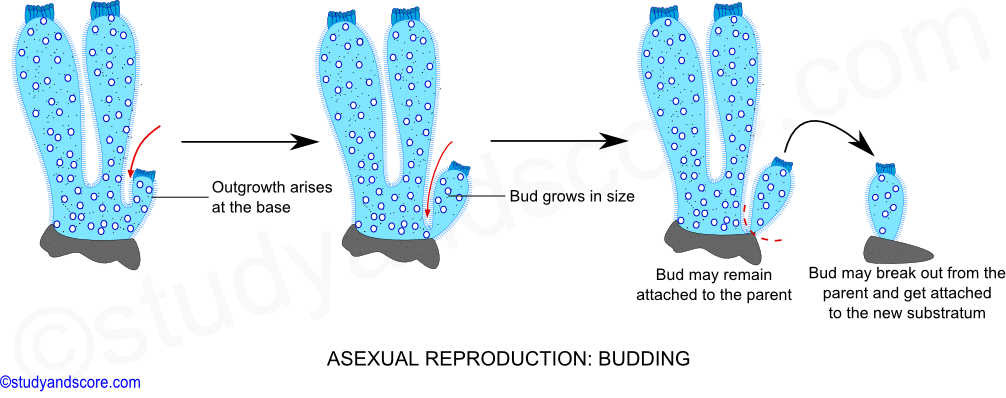
Phylum Porifera Sexual And Asexual Reproduction In Sponges And Regeneration In Sponges Study Score

Phylum Porifera Sexual And Asexual Reproduction In Sponges And Regeneration In Sponges Study Score

Asexual Reproduction Biology 2022
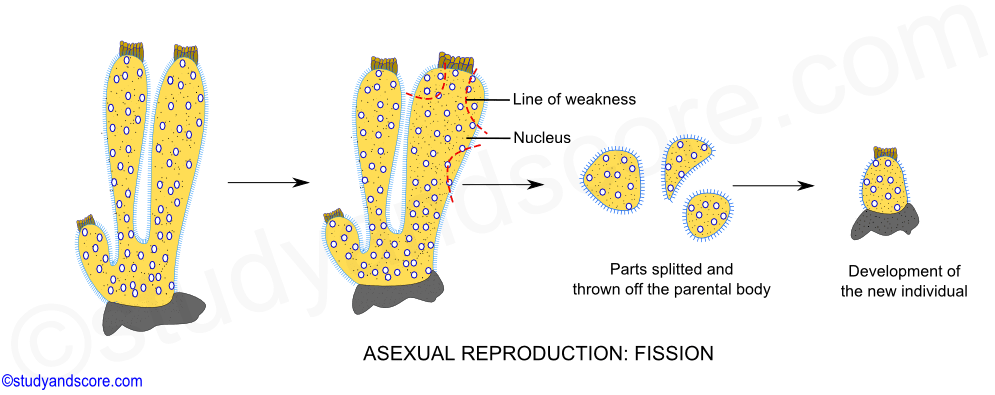
Phylum Porifera Sexual And Asexual Reproduction In Sponges And Regeneration In Sponges Study Score
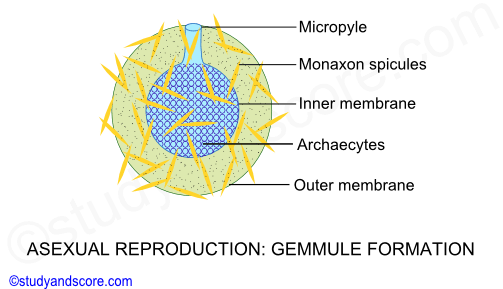
Phylum Porifera Sexual And Asexual Reproduction In Sponges And Regeneration In Sponges Study Score
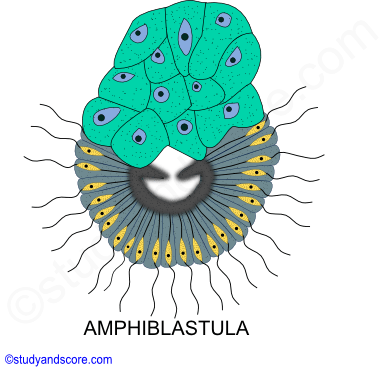
Phylum Porifera Sexual And Asexual Reproduction In Sponges And Regeneration In Sponges Study Score

Solved Block Date Name 7 Describe Asexual Reproduction Chegg Com
Reproduction In Animals Asexual And Sexual With Diagram Zoology


Comments
Post a Comment